View attacks 
The Attacks list shows all attacks that have occurred in an organization.
Select Attacks in the header.
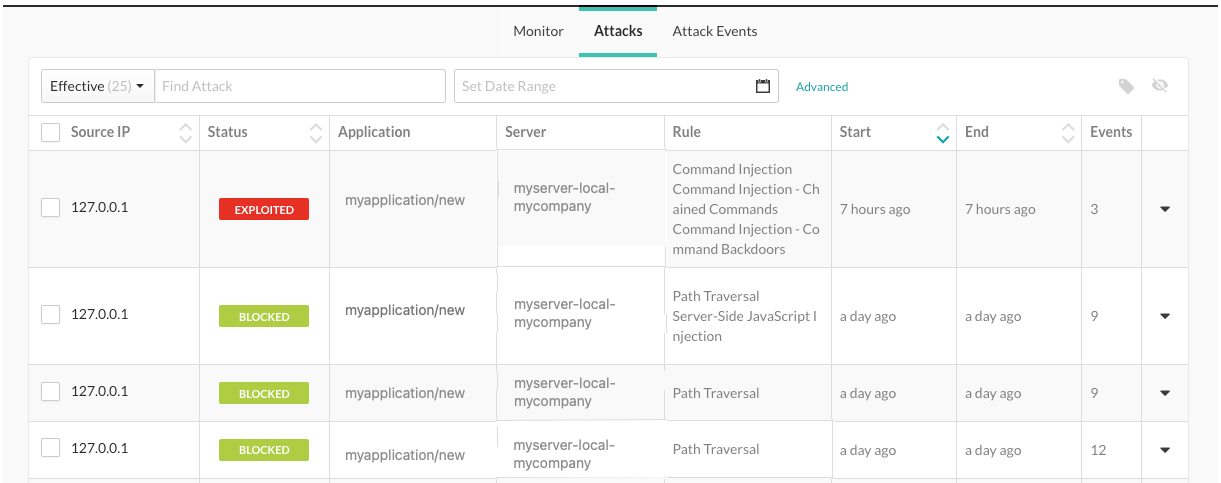
To view all attacks that occurred in your organization, select the Attacks tab.
To filer the view, select one of these filters:
All: Shows all attacks
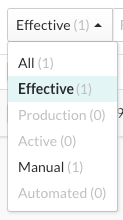
Effective: Shows attacks with a status of Blocked, Suspicious, and Exploited.
Production: Shows attacks that occurred in a production server
Active: Shows attacks that are currently in progress
Manual: Shows attacks that have less than 20 requests per second. It could indicate that a human is generating attacks.
Automated: Shows attacks that have more than 20 requests per second. It could indicate that a malicious bot is generating attacks.
To view more details on the attack, select source name or IP address in the Source IP column.
To see each attack event in the attack, select the Overview tab.
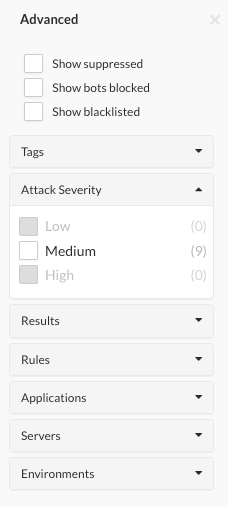
For more filters, select Advanced next to the date range and select a filter.
To see more details about the attack event, select Source IP.
To view the time of each event, under Attack duration, select See timeline.

To see more details including the rate of events, severity, and attacker, select the Notes tab.
To share or view communications with your team, select the Discussion tab.
Read existing comments or enter a new comment and click Add Comment.
Attack details
The attack data that Contrast displays includes these items:
Source IP: The IP address from which the attack is originating.
Status: The current status of the attack.
An attack status is determined by the highest severity status of the attack events within the attack. If any event has an Exploited status, the attack status will be Exploited. If there are no Exploited events, the status will be the next highest severity event's status. The severity order, starting with the highest, is:
Exploited: If Contrast detects and confirms a definite attack but the mode for the applicable rule is set to Monitor, Contrast does not block the request.
This status only applies to input tracing rules where Contrast is confident that an attack occurred. Confirmed attacks are those that met a high confidence threshold at the perimeter, or those that are watched and verified at the sink.
Suspicious: If Contrast detects an attack and the applicable rule reports the attack as suspicious, but the mode for the rule is set to Monitor, Contrast does not block the request. This status applies to non-input tracing rules, where Contrast is unable to verify that an attack occurred.
Blocked: If Contrast detects an attack and the mode for the applicable rule is set to Block, Contrast blocks the request.
Blocked (P): This status applies to rules that support both Block At Perimeter and Block modes.
If Contrast detects an attack before the application can process the request and the mode for the applicable rule is set to Block At Perimeter, Contrast blocks the request.
If Contrast detects an attack that is not at the perimeter, it blocks the request and the status is Blocked, even if the mode for the rule is set to Block At Perimeter.
Probed: If Contrast detects an attack but cannot confirm it and the mode for the applicable rule is set to Monitor, Contrast does not block the attack. Unconfirmed attacks are those that did not meet a high confidence threshold at the perimeter; they are watched but not detected at the sink.
Application: Specific applications that saw attack events from the IP address while the attack was active.
Server: Specific server that saw attack events from the IP address while the attack was active.
Rule: Any attack type identified from the IP address while the attack was active.
Start: The timestamp of the first attack event seen from the IP address during the attack time frame.
End: The timestamp of the last attack event seen from the IP address during the attack time frame.
Events: The number of attack events that comprise the attack.